Conflicts in Africa—Introduction
Author and Page information
- This page: https://www.globalissues.org/article/84/conflicts-in-africa-introduction.
- To print all information (e.g. expanded side notes, shows alternative links), use the print version:
Despite decades of conflict, death and tragedy, coverage of issues in Africa has often been ignored, oversimplified, or excessively focused on limited aspects. Deeper analysis, background and context has often been lacking, so despite what seems like constant images of starving children in famines, news of billions in aid to Africa from generous donor countries, the background context and analysis is often missing.
Whether aid makes the situation worse, or why there is famine and hunger in Africa when African nations are exporting crops to other parts of the world are rarely asked by the mainstream.
On this page:
- Africa Hardly Attracts Media Attention Despite Pressing Concerns
- Many Conflicts Throughout Africa
- Root Causes of Problems
- China and Africa; concerns over rights and exploitation
- Africa Maps Showing Modern and Pre-Colonial Areas
Africa Hardly Attracts Media Attention Despite Pressing Concerns
Recent years have seen many regions of Africa involved in war and internal or external conflict, from the seven or so countries directly involved in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) to the Sierra Leone crisis and the war in Ethiopia/Eritrea and the various other civil wars.
Virgil Hawkins, author of Stealth Conflicts; How the World’s Worst Violence Is Ignored (Ashgate, October 2008), provides a useful map representing conflict death tolls between 1990 and 2007 where the square area of continents/regions corresponds to their proportion of conflict death tolls:
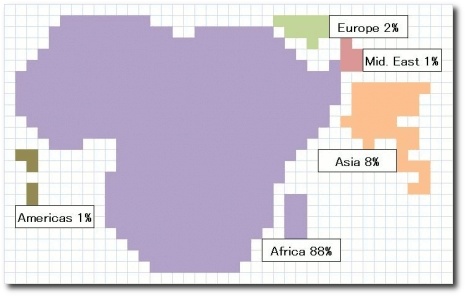
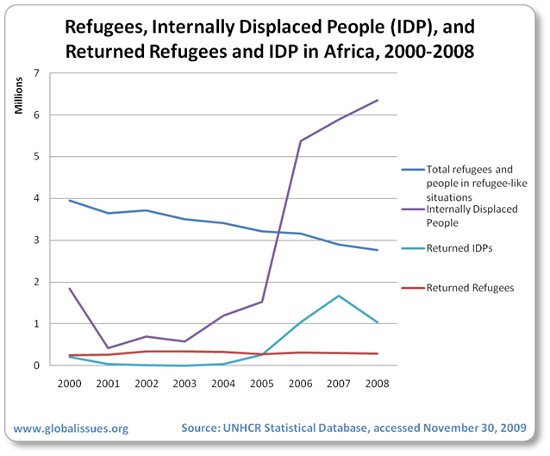
In addition to the conflict deaths, there have been over 9 million refugees and internally displaced people. While refugee numbers in recent years have declined, the number of internally displaced has risen:
If this scale of destruction and fighting was in Europe, then people would be calling it World War III with the entire world rushing to report, provide aid, mediate and otherwise try to diffuse the situation.
Yet here, as mentioned in the media section of this web site, and noted by Virgil Hawkins, the western mainstream media does practically nothing to raise this awareness (or, perhaps it is not deemed important enough to report extensively about).
Occasional coverage is provided, but not anywhere near the volume like we had seen during the build up and the ensuing crisis in Kosovo, or Iraq, or Palestine/Israel, each of which were serious conflicts, but in terms of deaths and displaced, were often far less than many conflicts in Africa.
Hawkins did a year long study (see above new world maps link) on some major western media outlets in 2000 to see what percentage of their media focus fell where. Disappointingly, and unsurprisingly perhaps, Africa did not even figure in 10% of the coverage.
In a separate article breaking down the conflict deaths since the end of the Cold War, Hawkins notes over 9 million of these deaths occurred in Africa, and adds:
It quickly becomes obvious that conflicts that have dominated the agendas of actors in a position to respond (policymakers, the media, the public and academia) are often relatively small in scale compared to many of those that have consistently failed to attract attention.
More coverage about issues concerning Africa can be found on the Internet than the traditional mainstream media outlets, but even then it is not as easy to find the information. Side Note(Since originally making this point in 1999, additional web sites from African organizations have emerged providing a lot of information, about news, cultures, and so on about all aspects of Africa. Even the popular press in the West are providing more information on African news, although these are often very brief and without the much needed perspectives and backgrounds from political, historical, socioeconomic angles etc.)
According to research from media organization Media Tenor, from 1 January 2002 until 30 June 2003, September 11 has turned the watch back to the pre-1990’s, virtually eliminating all events and issues that are not related to either the United States or its coalition partners—especially when reporting on conflicts.… conflicts and wars played the most important role in all analysed television stations in Britain, Germany and the United States. But subtracting from this coverage Iraq and Afghanistan, only 0.2% (n=507) of all reports (N=23587) focused on conflicts in Africa. Wars without the involvement of the Western nations, do not seem newsworthy enough to appear on international TV news agendas, and the little coverage given only focuses on the brutality of the conflict and not on possible solutions.
And citing Hawkins again:
The death toll from conflict in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) is literally one thousand times greater than that in Israel-Palestine, yet it is the latter that is the object of far greater media coverage … [and where] the intricacies and nuances of the conflict, political situation and peace process are almost obsessively analyzed and presented.… [African] conflicts are frequently brushed off and dismissed as being chaotic, or worthy of some vague pity or humanitarian concern, but rarely of any in-depth political analysis.
But even [when there is coverage of conflicts in] Africa, the death toll has little to do with the levels of coverage. Darfur made a rare appearance on the radar of Western concern in 2004 … at a time when the known death toll from conflict there was still 80 times smaller than that in the DRC. Similarly, political violence in early 2007 in Zimbabwe resulting in one death and a number of arrests and beatings of political leaders became the object of relatively high levels of attention and indignation in the Western media. At almost exactly the same time, political protest in Guinea was put down by government forces that fired indiscriminately into crowds of protesters resulting in a total of 130 deaths and numerous arrests. Also at the same time, street battles between government and opposition forces in the capital of the DRC resulted in between 400 and 600 deaths, and resulted in the exile of the opposition leader. Yet this violence in Guinea and the DRC was virtually ignored by the Western media.
But why is it important whether or not media outlets in countries such as those in the West provide coverage of African and other conflicts that do not appear to involve them?
- Background such as the colonial as well as post-World War II history, social and political context, international economic issues and much more are all perspectives needed to help people in the western nations and elsewhere to really begin to understand the present situations and issues in appropriate context. Simplistic views (at their simplest and crudest, they are even racist, intentional or not) offer little understanding of the complexities of causes, let alone a platform from which to form ideas on how to move forward.
- In international affairs, influential nations, such as many from western countries all have direct and indirect influences around the world, so it is important for such issues to be presented broadly and to see issues such as those in Africa with this context in mind.
- From a somewhat self-interest perspective (which, after all, most countries prioritize on, in international affairs), things happening far away have an impact on us. For example, J. Brian Atwood, former head of the US foreign aid agency, USAID commented that
failed states
(which included a number of African countries suffering from conflict)threaten our nation. They cost us too much. They create diseases that impact on us. They destabilize other nations. They stymie economic growth and they deny us economic opportunity in the largest new marketplace — the developing world.
(quoted from Esman and Herring, editors, Carrots, Sticks, and Ethnic Conflict; Rethinking Development Assistance, (University of Michigan Press, 2001), Chapter 3 USAID and Ethnic Conflict: An Epiphany? by Heather S. McHugh, p. 54.)
Many Conflicts Throughout Africa
There have recently been numerous civil wars and conflicts going in Africa, some of which are still going on, including
- Angola, which has seen an estimated 500,000 people killed since 1989 and an estimated 3 million refugees. It is also being torn apart due to resources such as diamonds and offshore oil, with various factions fighting for these prizes, supported by multinational corporations and other governments. See also the following:
- A Rough Trade; The Role of Companies and Governments in the Angolan Conflict, by Global Witness, December 1998. (Their web site has other reports on related issues as well.)
- The Zambian Connection: Ukrainian plane came to deliver UNITA diamonds? from the Monitor for Human Rights and Development, Issue 101, April 7-13 2000, also reports on the Diamond and Zambia connection.
- ANGOLA: Allegations of embezzlement of 'petrodollars', by IRIN, the U.N. Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs, 26 March 2002
- Algeria
- Burundi
- Congo
- The Democratic Republic of Congo
- Cote d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Eritrea/Ethiopia
- Liberia
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- Sierra Leone
- Sudan and South Sudan/Darfur
- Uganda
- Zimbabwe
Some of these nations are also involved in the war in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) and the DRC is also involved in some of these civil wars.
No less than 28 Sub-Saharan African states have been at war since 1980, as pointed out by international development organization, ID21.
When the missionaries came to Africa they had the Bible and we had the land. They said,
Let us pray.We closed our eyes. When we opened them we had the Bible and they had the land.
Root Causes of Problems
Political corruption, lack of respect for rule of law, human rights violations are all common reasons heard for some of the causes of Africa’s problems. Although, not the only reasons, some often overlooked root causes also include the following:
The Legacy of European Colonialism
European colonialism had a devastating impact on Africa.
The artificial boundaries created by colonial rulers as they ruled and finally left Africa had the effect of bringing together many different ethnic people within a nation that did not reflect, nor have (in such a short period of time) the ability to accommodate or provide for, the cultural and ethnic diversity. The freedom from imperial powers was, and is still, not a smooth transition. The natural struggle to rebuild is proving difficult.
Artificial Borders Created by Imperial Europe
In the 1870s European nations were bickering over themselves about the spoils of Africa. In order to prevent further conflict between them, they convened at the Berlin Conference of 1884-1885 to lay down the rules on how they would partition up Africa between themselves.
Between 1870 and World War I alone, the European scramble for Africa resulted in the adding of around one-fifth of the land area of the globe to its overseas colonial possessions.
Colonial administrations started to take hold. In some areas, Europeans were encouraged to settle, thus creating dominant minority societies. France even planned to incorporate Algeria into the French state, such was the dominance and confidence of colonial rulers at the time. In other cases, the classic divide and conquer
techniques had to be used to get local people to help administer colonial administrations. Some were only too willing to help for their own ends.
In most areas colonial administrations did not have the manpower or resources to fully administer the territory and had to rely on local power structures to help them. Various factions and groups within the societies exploited this European requirement for their own purposes, attempting to gain a position of power within their own communities by cooperating with Europeans. One aspect of this struggle included what Terrence Ranger has termed the
invention of tradition.In order to legitimize their own claims to power in the eyes of both the colonial administrators, and their own people, people would essentially manufacturetraditionalclaims to power, or ceremonies. As a result many societies were thrown into disarray by the new order.
(This site’s section on Rwanda notes how this invention of tradition was one of the contributing factors to the eventual genocide, as well as other factors.)
Throughout Africa, Europe staked a claim. Many post war conflicts, such as that in Uganda, had a some root cause in this scramble for Africa as a documentary called Uganda Rising notes:
Colonialism, in the traditional sense, ended as European countries started fighting over themselves over the world (the World Wars) and in effect, weakened themselves in the process (allowing the United States and Soviet Union to eventually gain in immense power. They would spend another 50 years continuing that fight). Colonized people, the world over, saw their chance to break free as they realized that Europe was not invincible or as civilized as they claimed. Britain could no longer hold on to India, for example. In Africa,
a sense of local patriotism or nationalism took deeper root among African intellectuals and politicians. Some of the inspiration for this movement came from the First World War in which European countries had relied on colonial troops for their own defence. Many in Africa realized their own strength with regard to the colonizer for the first time. At the same time, some of the mystique of the
invincibleEuropean was shattered by the barbarities of the war. However, in most areas European control remained relatively strong during this period.
The natural struggle to rebuild is proving difficult
Some have commented that pointing to colonialism is not an excuse as many African countries have had decades to try and resolve this. The implication of the argument is that the effects of centuries of colonialism, in effect, are supposed to be overcome in just a few short years. Yet, as Richard Robbins, professor of anthropology suggests, if countries like Canada have been struggling with accommodating different groups, then in Africa the problem is more complex:
We must remember that the European agreements that had carved up Africa into states paid little attention to cultural and ethnic boundaries and ethnic groups had little opportunity or need to form political alliances or accommodations under repressive colonial rule.… Think of countries such as Canada, which has been trying for hundreds of years with mixed success to accommodate only two linguistic groups — English and French — and you get an idea of the problems of African states with far greater cultural and linguistic divisions.
Furthermore:
Consider the extent to which he Second World War of just 6 years duration has pervaded the consciousness of our developed world for 2 generations and imagine how 4 centuries of enslavement might have seized the entire social and cultural ethos of an undeveloped continent.
In some parts of Africa, slavery and/or colonial administration had almost erased cultures and community with an education
and civilizing
program that gave Africans only a minimal skill set that served European colonial interests. Rebuilding from decades and centuries of this has been a tough struggle.
Consider the following from a speech by Bob Gelfdof:
To establish a type of nationwide government, [European] colonial administrators effectively set about inventing African traditions for Africa, that would make the process more acceptable to the indigenous population. The most far-reaching inventions of tradition in colonial Africa occurred when the administrators believed they were respecting age old African custom whereas a commentator notes
What were called customary law, customary land-rights, customary political structure and so on were in fact all invented by colonial codification.By creating an image of Africa steeped in unchanging tradition the colonizers condemned the continent to live in a reconstructed moment of its past. A vast continental theme park — Africa-land, that hindered development for decades. But perhaps the most pernicious of the traditions which the colonial period bequeathed to Africa was the notion of Tribalism. Just as every European belonged to a nation, every African must belong to a tribe, a cultural unit with a common language, a single social system and established customary law. In Zambia the chief of a little known group once remarked,My people were not Soli until 1937 when the Bwana D.C. told us we were. The concept of the Zulu as a discrete ethnic group did not emerge until 1870.These were the dangerous sands upon which the colonialists imposed a new political geography. However once in motion, the process was enthusiastically reinforced by the Africans themselves. Tribes became the object of passionate African imagination. Some chroniclers have endowed their tribes with a retrospective primordial essence. Rather like Yeats did with the similarly disenfranchised Irish.
The British ruled through these local hierarchies, a process which unconsciously promoted the most malleable, collaborative or corrupt local chiefs and where none existed, as we've seen, they simply created one, enabling ambitious individuals and groups to achieve positions of status, dominance, and wealth that might otherwise have been unattainable.
To counter this tribalism some African leaders proclaimed the single party state to be the only means to control the excessive, ethnically based competition for the global goods of modernity — education, health, and the eradication of poverty. Competitive democracy they said would only lead to penury. Yet one-party rule unrestrained by the moral check of shared community had the same result. It proved to be a mask for oppression, ethnocracy and kleptocracy. Of the 107 African leaders overthrown between 1960 and 2003 two-thirds were murdered, jailed or slung into exile. Up until 1979 59 African leaders were toppled or assassinated. Only three retired peacefully and not one was voted out of office. No incumbent African leader ever lost an election until 1982.
… imposing … cultural beliefs on other people, whether by economic muscle or cruise missile, so that they can be more like us is a farce, particularly when the obvious external purpose is regional control of resources and political influence.
Unequal International Trade; Comparative Disadvantage
Colonialism had thus transformed an entire continent. Vast plantations and cash crop-based, or other extractive economies were set up throughout. Even as colonial administrators parted, they left behind supportive elites that, in effect, continued the siphoning of Africa’s wealth. Thus has colonialism had a major impact on the economics of the region today. Various commentators, mostly from the third world observer that colonialism in the traditional sense may have ended, but the end results are much the same.
An interview with former Tanzania President, Julius Nyerere captures some of this:
I was in Washington last year. At the World Bank the first question they asked me was
how did you fail?I responded that we took over a country with 85 per cent of its adult population illiterate. The British ruled us for 43 years. When they left, there were 2 trained engineers and 12 doctors. This is the country we inherited.When I stepped down there was 91-per-cent literacy and nearly every child was in school. We trained thousands of engineers and doctors and teachers.
In 1988 Tanzania’s per-capita income was $280. Now, in 1998, it is $140. So I asked the World Bank people what went wrong. Because for the last ten years Tanzania has been signing on the dotted line and doing everything the IMF and the World Bank wanted. Enrollment in school has plummeted to 63 per cent and conditions in health and other social services have deteriorated. I asked them again:
what went wrong?These people just sat there looking at me. Then they asked what could they do? I told them have some humility. Humility — they are so arrogant!… It seems that independence of the former colonies has suited the interests of the industrial world for bigger profits at less cost. Independence made it cheaper for them to exploit us. We became neo-colonies.
International trade and economic arrangements have done little to benefit the African people and has further exacerbated the problem. IMF/World Bank policies like Structural Adjustment have aggressively opened up African nations with disastrous effects, including the requirements to cut back on health, education (and AIDS is a huge problem), public services and so on, while growing food and extracting resources for export primarily, etc, thus continuing the colonial era arrangement.
The resulting increased poverty of Sub-Saharan Africa and the immense burden of debt has further crippled Africa’s ability to develop.
While the previous links can provide far more details, consider the following overview from Bob Geldof:
[The] theory of comparative advantage … says that a country produces that which it can produce cheaper than any other and sells it to others in exchange for that which they can produce cheaper than us. The invisible hand of the market will of itself sort out any inequities in this system allowing for the appropriately correct level of development to any particular producer. The [European] colonies distorted this view by deciding that Africa’s comparative advantage was its poverty, like we do today with our global brand footwear, clothing etc. As a result in Africa, existing patterns of farming were wiped away and huge plantations of single non-native crops were developed, always with the need of European processing industry in mind. There was a global transfer of foreign plants to facilitate this — tea, coffee, cocoa, rubber etc., The result was the erosion of the soil, forerunner of the desertification evident today. And with the erosion came steadily decreasing quantities of already scarce local food grown on marginal lands by labourers working for pitiful wages. This concentration on a few major cash crops or the extraction of an important mineral source left the countries on independence incredibly vulnerable to dramatic fluctuations in the prices of those commodities on the world market.
Adam Smith also suggested that the market was free within reason. It could never be laissez faire. Indeed he suggested infant economies be protected from the chill winds of the financial gales as we did in our development but prevented in others. The Navigation Acts the were wholly anticompetitive policies — which at that time prevented American colonists from making their own woollen or iron goods, and were like their equivalent today when we [the developed world] impose on a Third World producer of pineapples who wants to sell in the EU a tariff of 9% for fresh fruit, 32 % for tinned pineapples and 42% for pineapple juice — planting the seeds of today’s disparities between Northern and Southern economies.
Limited rights to land also prevents a chance for successful development, as Oxfam details.
Cold War by Proxy; Supporting and Arming Dictatorships in Africa
Throughout the Cold War, major powers such as the U.S.A, the Soviet Union and others supported various regimes and dictatorships. Some possibly promising leaders in the early days of the independence movements throughout the Third World were overthrown. There was disregard from the major powers as to how this would affect the people of these countries. ($1.5 billion worth of weapons to Africa has come from the U.S. alone, according to a report from the World Policy Institute, while Europe for example, was able to exploit Africa’s resources
to help rebuild after World War II.)
The proliferation of small arms in the region when the Cold War ended has helped fuel many conflicts.
Africa has become an attractive and profitable dumping ground for nations and arm manufacturers eager to get rid of weapon stocks made superfluous by the end of the Cold War or by technological developments.
Corporate Interests, Exploitation, Corruption and Other Issues
As the companies duel, countries and communities often find themselves in the crossfire.
Corporate interests and activities in Africa have also contributed to exploitation, conflict and poverty for ordinary people while enriching African and foreign elites.
The easy access to natural resources to maintain and fuel rebellions (combined with corporate interests) makes for a nasty combination.
A lack of support for basic rights in the region, plus a lack of supporting institutions, as well as the international community’s political will to do something about it and help towards building peace and stability has also been a factor. A World Bank report notes that politics and poverty cause civil wars, not ethnic diversity.
It also points out that in Africa, failed institutions are also a cause. It adds that where there is ethnic diversity, there is actually less chance for civil wars, as long as there is not just a small number of very large ethnic groups, or ethnic polarization.
These And Other Causes Reinforce Each Other
For the June 2002 G8 summit, a briefing was prepared by Action for Southern Africa and the World Development Movement. In that, they also pointed out similar causes to the above, when looking at the wider issue of economic problems as well as political:
It is undeniable that there has been poor governance, corruption and mismanagement in Africa. However, the briefing reveals the context — the legacy of colonialism, the support of the G8 for repressive regimes in the Cold War, the creation of the debt trap, the massive failure of Structural Adjustment Programmes imposed by the IMF and World Bank and the deeply unfair rules on international trade. The role of the G8 in creating the conditions for Africa’s crisis cannot be denied. Its overriding responsibility must be to put its own house in order, and to end the unjust policies that are inhibiting Africa’s development.
Blame the VictimSummit, Action for Southern Africa, June 25, 2002. (You can see the briefing in full (PDF format) from this link.)
The G8 section on this web site also looks in more detail at the way Western nations appear to have offered to help Africa, e.g. through wiping out their debts, but that in reality it turns out far less has actually happened, and that G8 nations are amongst the ones that have actually played a big role in Africa’s current problems.
Hence, as well as looking into the urgent and critical issues of corruption, mismanaged leadership and governance in Africa, external factors resulting from geopolitical power play must also be considered.
China and Africa; concerns over rights and exploitation
Criticism of China’s human rights is (predictably) increasing in the West, as China rises. Some of the concerns are genuine, while others may hide political agenda. Common criticisms are over areas such as human rights, environment, and labor standards. As Chinese enterprises expand overseas, especially in Africa, criticisms of exploitation are increasing.
For example, China’s silence on the Sudanese government’s policy in Darfur suggests that China is not concerned about human rights; just about its own economic interests. In Angola for example, where there are lots of oil interest (not just from China), some Chinese companies have been accused of ignoring local issues, for example by importing many materials from China rather than sourcing it locally, and even hiring Chinese only, excluding local Angolans.
A BBC television report in early July 2007 even noted that at an African/Chinese conference, the West was not there, implying the West could perhaps have been able to tame Chinese attempts at exploitation. Nothing was mentioned about the decades of Western exploitation of Africa that continues today albeit more benignly.
A BBC web site forum even asked, Is China Africa’s new master?, perhaps not realizing that by saying new
, it appeared to acknowledge a role that the West currently attempts to fill.
It seems that there may be some double standards here.
As detailed on this site’s section on Africa and trade, economics, and poverty issues, these western nations are the very ones that have exploited Africa for many decades. Some of these nations have even overthrown potential or fledgling democracies, favoring brutal dictators that have bled their countries.
For example, the economic policies of the IMF and World Bank, backed by Washington and Europe have been very detrimental to Africa. From Structural Adjustment Policies to economic dumping (often called food aid) to other aspects of unfair aid, debt and trade deals presented as historic positive deals for Africa, these issues seem to have been ignored when raising concerns about China’s involvement (or, as the previous link also notes, are ignored even when discussing Africa).
Firoze Manji, editor of the popular pan-African social issues web site, Pambazuka News, also raises the important point that in comparison to Europe and the US, China in Africa is still a small player.
It is worth quoting Manji at some length:
… in comparison to Europe and the US, China in Africa is still a small player. While keeping an eye out on China, Africans should not be distracted from paying attention to the West's continued exploitation of the continent including the use of military might to protect its economic interests.
…
Open any newspaper and you would get the impression that the African continent, and much of the rest of the world, is in the process of being ‘devoured’ by China. Phrases such as the ‘new scramble for Africa’, ‘voracious’, ‘ravenous’ or ‘insatiable’ ‘appetite for natural resources’ are typical descriptors used to characterise China’s engagement with Africa. In contrast, the operations of western capital for the same activities are described with anodyne phrases such as ‘development’, ‘investment’, ‘employment generation’.
…
China’s involvement in Africa has three main dimensions: foreign direct investment, aid and trade. In each of these dimensions China’s engagement is dwarfed by those of US and European countries, and often smaller than those of other Asian economies.
After going into further detail (worth reading) Manji concludes that China offers potential for Africa which some Western countries finds threatening, but at the same time is taking advantage of the more open environment:
China has the advantage of never having enslaved or colonized the continent. China has also not made any false promises coated with neo-liberalism. While the West, the IMF and the World Bank put conditions that only aid in their fleecing of Africa, China has so far been willing to provide unconditional aid and invest in infrastructure. At the same time, however, it freely takes full advantage of the opening up of markets that neo-liberal economic policies over the last 25 years have offered, unencumbered.
And so far, unlike the US, China has not sought to establish military bases in Africa to protect its economic interests, which the US has sought to establish through AFRICOM.
Many western news outlets and campaigners are quick to point out that China offers aid with no strings attached, whereas western nations offer aid with conditions tied to human rights. While there is some truth to this, it is often overlooked that a lot of conditions by western countries are not about human rights, but about opening up African economies and it is these conditions that are often criticized.
Inter Press Service (IPS) noted some problems with a huge deal between China and the Democratic Republic of Congo in 2008. The deal involved China pledging a $9 billion loan as well as building massive new copper and cobalt mines, 4,000 km of roads and railways, upgrading Congo’s beleaguered mining sector, as well as build schools, hospital and clinics. In return, Beijing secured copper and cobalt concessions that over 25 years would supply Chinese manufacturing with 6.8 million tons of copper and 620,000 tons of cobalt.
It was dubbed by Kinshasa as Congo’s Marshall Plan, but the IMF and Western powers didn’t appear to like it, pressuring (and succeeding) Congo to renegotiate for $6 billion under the threat of losing aid from the IMF and the West. Some bonus money ($23 million) from Chinese companies to their Congolese counterparts seems to have gone missing leading to a lot of criticism of China. The amount of criticism this generated led China to wonder if the West was trying to undermine its presence there.
When interviewed by IPS Shen Jiru, an expert on international relations with the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences argued that China was providing free-interest [sic] loans and aid and we are a reliable backup for Africa’s economic development.
According to IPS, in 2009, China pledged to give Africa 10 billion dollars in concessional loans over the next three years, and is accelerating its drive to pour vast sums of money into developing infrastructure in many African nations. This has been welcomed by African leaders. For instance, Ethiopia’s Prime Minister Meles Zenawi, speaking at the World Economic Forum on Africa held in Tanzania in May 2010, said China’s interests were consistent with those of African countries striving to overcome the legacy of reliance on commodity exports and move towards industrialization.
It made sense for China to spend in Africa, Zenawi felt, because its massive foreign exchange reserves are largely denominated in dollars, and Beijing needs to diversify those assets. It’s in their interest to spend tens of billions of dollars in Africa and it’s in our interest to have access to those tens of billions of dollars.
So, it seems that Africans should be cautious about China’s interests in Africa, but also be aware that criticism levied against China by others such as various Western countries may also have double standards and be part of a wider agenda whereby the rich countries are feeling threatened by the rise of a potential economic competitor. Western standards of human rights and raising those as issues are a good thing, but their own aid policies have often been with their own interests in mind, so caution is probably warranted for anyone bearing gifts.
Africa Maps Showing Modern and Pre-Colonial Areas
The two maps below, courtesy of Black Studies Library (BSL), Empathos National Library, show the partitioning of Africa.
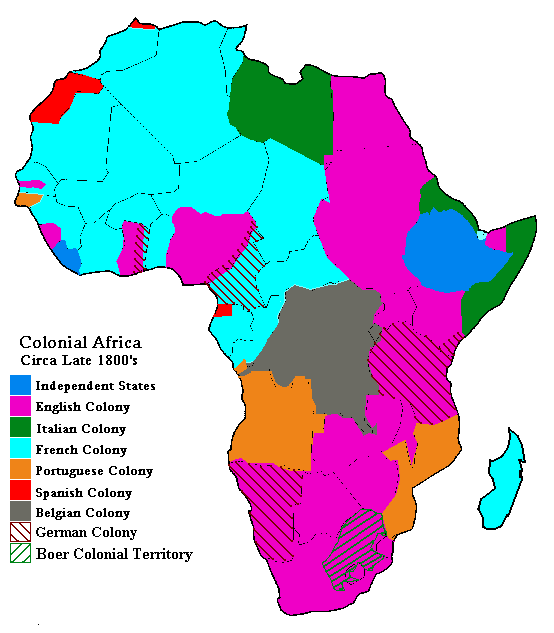
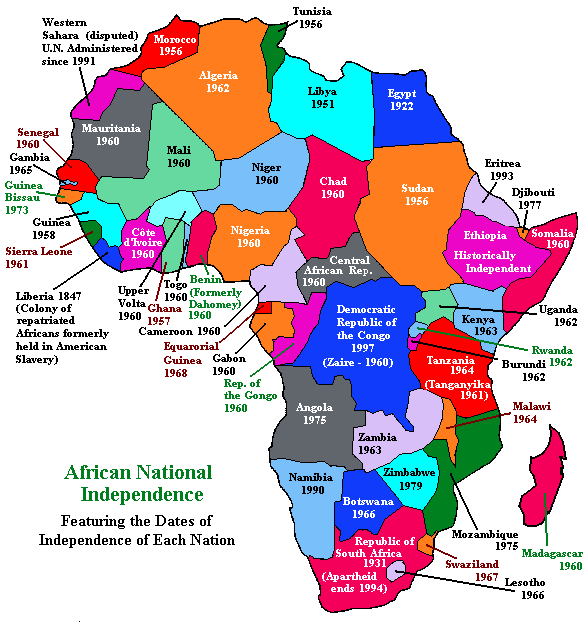
For more maps, check out
- The Maps from the Black Society Library. They provide some interesting historical insights into the region.
- Map of Africa from World Sites Atlas provides a clickable map of Africa that allows you to see information for each country.
Author and Page Information
- Created:
- Last updated:
 Global Issues
Global Issues