Himalayan Monsoon Disaster: Climate Change Colludes with Bad Development
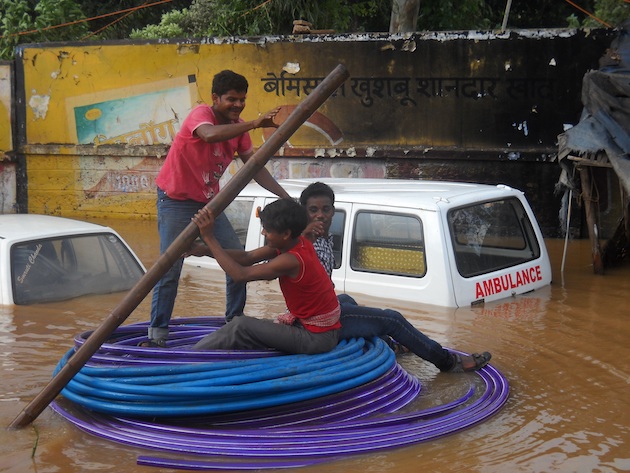

BHUBANESWAR, INDIA, Aug 15 (IPS) - As torrential rains, cloudbursts, floods, and landslides continue to wreak colossal damage and claim lives in Himachal Pradesh, India’s Himalayan foothill provinces. The question everyone is asking is: why is this happening?
Himachal Pradesh received 250 millimetres or ten inches of rain in just four days, between 7 to 11 July, which accounted for almost 30 percent of the total monsoon rainfall in a year. This sent mountain rivers spilling over their banks into villages and towns and caused widespread flash flooding, mud, and landslides.
Over the whole month of July, the State received 71 percent excess of 438 mm actual rainfall against 255.9 mm normal rainfall. It is the second-highest rainfall in 43 years, since 1980, according to the government's meteorological department.
Himachal Pradesh has witnessed a six-time increase in major landslides in the past two years, with 117 occurring in 2022 as compared to 16 in 2020, according to data compiled by the State disaster management department.
This year until now, the state witnessed 79 landslides and 53 flash flood incidents, with the monsoon only halfway, arriving in late June, as per the developing data.
There have been 223 deaths from these disasters to date. Cloudbursts and losses continue in Himachal Pradesh. Even on August 10, a family of 5 were buried under their collapsed home.
Is Faulty Ecological Development Worsening the Damage?
A video that has gone viral worldwide sums up not just the magnitude of destruction but answers some of the reasons why. The video opens with loud panic calls as a thickened river of muck and huge logs swerve downhill monstrously into a narrow village lane flanked by rows of shops in Thunag village in the Mandi district of Himachal Pradesh.
Locals claimed the trees are Himalayan Cedars chopped down in tens of thousands to widen highways as the government rapidly develops its mid-hills as go-to summer holiday destinations for tourism.
Trees from forest land cleared for roads, tunnels and hydro-power dams are disposed on hill slopes, in rivers banks and streams along with the earthen muck and debris, said Tikender Singh Panwar, a city administrator who had earlier held office.
The course of the rivers has narrowed down, and the riverbeds filled up with silt, causing them to break banks much sooner than they normally would when torrential rains come.
Both tourism and hydro-electricity sectors are the highest earners for the government and are currently being developed on priority.
The planned development is responsible for this colossal damage, is not so much climate shift, Panwar categorically says. An urban specialist and earlier deputy mayor of Shimla, the State’s summer capital, Panwar, says the focus of Himachal Pradesh, with a fragile Himalayan ecosystem, is on (risky) exploitation of natural resources of water, forest, and nature to pull in more State income.
Traditionally, mountain regions for building infrastructure were not cut with vertical slits but terraced to minimise instability in these geologically vulnerable regions. Unfortunately, in a hurry to complete projects, mountains have been cut into vertically, leading to landslides, according to Panwar.
The government’s Himachal Pradesh State Disaster Management Authority agrees. “Vulnerability of the geologically young and not-so-stable steep slopes in various Himalayan ranges has been increasing at a rapid rate in the recent decade due to inappropriate human activity like deforestation, road cutting, terracing and changes in agriculture crops requiring more intense watering.”
Land use change is another trigger being viewed as causing a natural disaster to become more damaging. Spreading concrete infrastructures, including “river-view” hotels and homestays, encroach on the riverbanks and basins.
Cement plants have proliferated to meet the demand for leap-frogging constructions.
When more rainfall lands in an area than the ground can absorb, or it falls in areas with a lot of impermeable surfaces like concrete and road asphalt that prevent absorption, the water runs downhill, gathering force and everything on its way, turning streams and rivers into raging torrents. It seeks the lowest point in a potential pathway, often reclaiming its own encroached space – the river basin.
In India’s mostly unplanned urban areas, these often are roads, parking lots, slum settlements, and even multi-storied shops and homes. Changes in land use and land cover contribute to acerbate disaster damage.
Sand mined illegally from riverbanks to keep pace with the high demand from construction activities could also have played a role in the devastation that rivers caused in Himachal Pradesh, environmental activists said.
Question Mark on Hydro-Power Projects in Fragile Himalayan Region
Hydropower is the biggest source of income for Himachal Pradesh, with the national government having a major stake. The State has five major rivers. It sells electricity to other states. Rural electrification, too, remains a major focus. But the environmental cost of the dams in the Himalayan region may be high and already being experienced, said activists.
The State’s hydroelectricity potential is high, around 27,436 megawatts, which is 25 percent of the national potential. Of this, 10,519 MW is harnessed so far. More projects with lengthy tunnels to channelise river flow are being added quickly. “Sometimes the course of rivers was diverted to build dams for hydro-power projects. This is like playing with nature, says Panwar.
By 2030, some 1088 hydropower projects are planned to generate 22640 MW of electricity, according to Panwar. India has committed to achieving 500 Gigawatts of renewable energy by 2030.
This is raising alarm bells for more impending disasters.
In a Warming Asia: The Role of Climate Change in Increasing Water Disasters
When the cloudburst in the Thunag area dumped torrential rains, locals said they had no warning. But cloudbursts are characteristically localised, and sudden torrential rainstorm phenomena, categorised when rainfall is 100 millimetres per hour, have been increasing.
Cloudbursts occur when warm air currents block rain from falling, causing an accumulation of moisture. When the upward air currents become weak, the cloud dumps rain.
Flash flooding similarly occurs after excessive rainfall pours down in less than six hours. Both are unexpected and often catch victims unprepared.
The role of climate change is becoming increasingly evident in these types of deluges across continents.
The simplest part of the explanation for a complex phenomenon is that warmer temperatures lead to increased evaporation. This leads to extra moisture in the atmosphere, which in turn leads to heavy rainfall, especially when two weather systems coincide in a high-altitude, mountainous region. This is what happened in Himachal Pradesh in early July.
A low-pressure weather system carrying moisture all the way from the Mediterranean Sea to northern India, known as a Western Disturbance, coincided with the normal monsoon system, together resulting in torrential rain. This is not abnormal and, as such, not attributable to changing climate.
However, studies by scientists around the world show that the climate shift is intensifying the water cycle and will continue to intensify as the planet warms. A number of factors are intensifying the water cycle, but one of the most important is that warming temperatures raise the upper limit on the amount of moisture in the air. That increases the potential for more rain.
An international climate assessment in 2021 documented an increase in both wet extremes, including more intense rainfall over most regions, and dry extremes. These will continue to increase with future warming.
In India’s Himalayan region, with its complex terrain and varied weather patterns, deep, intense convective clouds form under normal circumstances. However, studies find instances of deep convection have increased over recent years. Sixty-five percent area in the Himalayan States now shows a trend towards ‘daily extreme rainfall’ categorised when 15 cm of rain falls in 24 hours. Climate change is thought to be one of the main causes of this, according to Madhavan Rajeevan, a senior retired official of India’s Ministry of Earth Sciences. “This can have severe consequences,” he says.
According to the International Disaster Database (EM-DAT), Asia is the world’s most disaster-impacted region; 83 percent of the 81 weather, climate, and water-related disasters in Asia in 2022 were flood and storm events. More than 50 million people were directly affected.
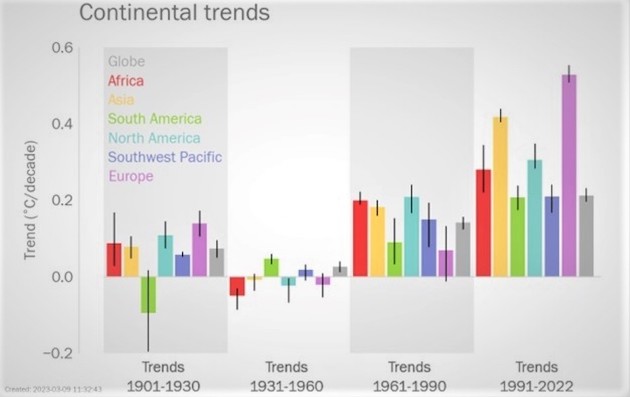
WMO State of the Climate in Asia 2022 report released in July said Asia, the largest continent with 30 percent of Earth’s land area, is warming faster than the global average. The warming trend in Asia in 1991–2022 was almost double the warming trend in the 1961–1990 period (see chart), according to the World Meteorological Organisation report.
IPS UN Bureau Report
Follow @IPSNewsUNBureau
Follow IPS News UN Bureau on Instagram
© Inter Press Service (2023) — All Rights Reserved. Original source: Inter Press Service
 Global Issues
Global Issues