Climate Change is No 'Future Scenario' for Pacific Island Nations; Climate Change is 'Real'
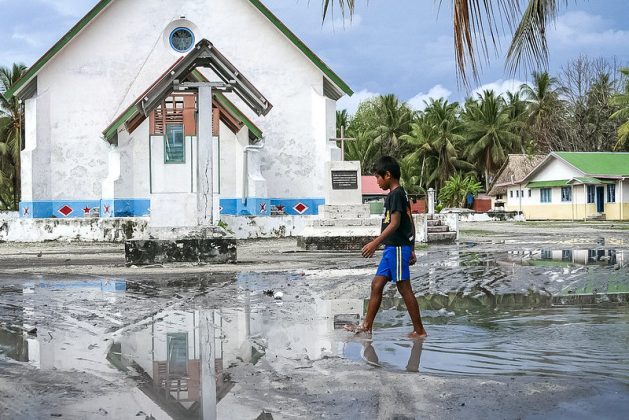

SHARM EL SHEIK, Nov 15 (IPS) - Pacific island countries are highly vulnerable to climate change, and several have disappeared – and more could sink under the sea owing to a rise in water levels.
According to UN figures, severe climate-change-induced weather conditions are already leading to the displacement of about 50 000 people each year. Urgent assistance is needed to help them adapt and lessen its impacts.
COP27 opened with an impassioned plea by Tuvalu Prime Minister Kausea Natano, who called for a fossil fuel non-proliferation treaty at COP27. Addressing the world leaders, he said: “Tuvalu has joined Vanuatu and other nations in calling for a Fossil Fuel Non-Proliferation Treaty to steer our development model to pursue renewables and a just transition away from fossil fuels.”
A losing battle against climate damage
In 2015, the Island of Vanuatu was hit by a category five cyclone that killed residents, displaced thousands and damaged infrastructure. It was not to be the last. Another severe cyclone hit the island in 2020 after buffeting the neighbouring Solomon Islands.
Vanuatu is one of 20 countries that make up the Pacific Islands. They have a population of more than 2 million whose livelihoods are tied to the sea. The island nations face a future underwater if they cannot cope with the impacts of climate change and repair the damage it has already caused.

“In Vanuatu, adaptation is a core issue to ensure we build resilience; otherwise, we will continue to see Vanuatu destroyed by cyclones and going under the sea,” says Nelson Kalo, a Senior Mitigation Officer in the Ministry of Climate change in Vanuatu, on the sidelines of COP27.
Kalo says climate change-induced natural disasters are impacting the area.
“We need resources to build our adaptive capacity so that in the future, we will be resilient to climate change,” he said.
Sea level rise, increasing temperatures and frequency and intensity of tropical cyclones, and storm surges are some of the climate change impacts facing island nations, some of which are in low-lying areas of just 5 meters above sea level at the highest point.
“In the Pacific Islands, the people are dependent on primary sectors, particularly agriculture and fishing, for their livelihoods, and we are seeing a variety of climate change effects across the region which are having impacts on livelihoods,” says Dirk Snyman, Coordinator of the Climate Finance Unit at the Pacific Community (SPC). The SPC is an international scientific and technical organization in the region that supports the rights and well-being of Pacific islanders through science and knowledge.
Ocean acidification and warming are affecting fisheries and causing the bleaching of coral reefs, which provide habitat for fish, a key source of food for islanders.
“In the Pacific islands, climate change is not some predicted future scenario based on projected models; it is a daily lived reality,” Snyman tells IPS. “It is becoming more and more difficult, particularly with crops and drinking water, for people to meet their daily needs that they now rely on imported food and drinking water, which come at a high cost."
Snyman said the island nations had incurred economic and non-economic losses, such as cultural losses, and that a loss and damage facility is a timely intervention for them. The issue of loss and damage fund has made it on the agenda of the COP27 negotiations, which intensify this week in Egypt.
Mitigation
Pacific island countries have very low emissions and emit less than 1 percent of global emissions as a region. But despite these low emissions, the countries have developed ambitious Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement to be fully renewable in terms of energy by 2030.
“Compare that to any NDCs throughout the world … (Yet) Pacific island countries are struggling to get money for transitioning to renewable energy because the argument is always that they are too small or they have too little emission reduction, so they are not receiving the money to finance their NDCs,” Snyman said.
The climate financing needs for the Pacific Islands are estimated at between 6.5 and 9 percent of GDP per year, which is around 1 billion US dollars per year.
Snyman said current estimates of approved financing are around 220 million US dollars annually, which is only 20 percent of the 1 billion US dollars needed. He said multilateral mechanisms take up to five years to get financing, by which time countries would have experienced the worst impacts of climate change.
“Pacific countries feel very strongly that money should be made for loss and damage to compensate for these economic and non-economic losses that are unavoidable and that they cannot adapt to and that will continue to affect communities for decades,” said Snyman.
Espen Ronneberg, Senior Adviser, Multilateral Climate Change Agreements at SPC, says loss and damage will occur without ambitious mitigation action and reductions in GHG emissions.
“We are already experiencing some of these things to a certain extent in that the impacts are being felt right now, but we are also looking into the future and how those impacts will get much worse unless mitigation is ramped up and unless technical assistance, finance, for instance, are also ramped up,” said Ronneberg, who explained that available resources were not fit-for-purpose in addressing the current impacts of climate change in pacific island countries.
Ronneberg said Pacific island countries were ambitious regarding mitigation as they have some of the world's highest energy costs due to fuel and natural gas importation costs. They have looked at energy efficiency through solar voltaic technology and are exploring wind and wave power.
“We have to look at the slow onset of impacts like sea level rise and changes in rainfall patterns. There may be opportunities for adaptation, but there is a point where you can no longer adapt – where an island becomes unliveable because of conditions,” he said.
Anne-Claire Goarant, Manager of the Climate Change and Environmental Sustainability Division at the SPC, said adaptation was vital for implementing the NDCs in the Pacific islands but that there is a need to focus on robust mitigation programmes.
“We need the flexibility to describe the adaptation objectives to reflect the reality on the ground, and at this stage, we need transformative action,” Goarant told IPS. “We have to speed up the scale and amount of money that is available to implement action that will deliver some results in the short and long terms, for example, planting trees on a massive scale along the shores.”
“It is not just a small dot of adaptation action; we really need a global goal that can be implemented at a local level by local communities because the work will be done locally by the people who need to understand what climate change is and why it is important to adapt and how they can be supported.”
IPS UN Bureau Report
Follow @IPSNewsUNBureau
Follow IPS News UN Bureau on Instagram
© Inter Press Service (2022) — All Rights Reserved. Original source: Inter Press Service
 Global Issues
Global Issues