Solar Energy Benefits Children and Indigenous People in Northern Brazil

BOA VISTA, Brazil, Dec 13 (IPS) - Solar energy is booming in Roraima, a state in the far north of Brazil, to the benefit of indigenous people and children in its capital, Boa Vista, and helping to provide a stable energy supply to the entire populace, who suffer frequent electricity shortages and blackouts.
The local government of Boa Vista, a city of 437,000 people, installed seven solar power plants that bring annual savings of around 960,000 dollars.
"We have used these savings to invest in health, education and social action, which is the priority of the city government because we are 'the capital of early childhood’," said Thiago Amorim, municipal secretary of Public Services and Environment.
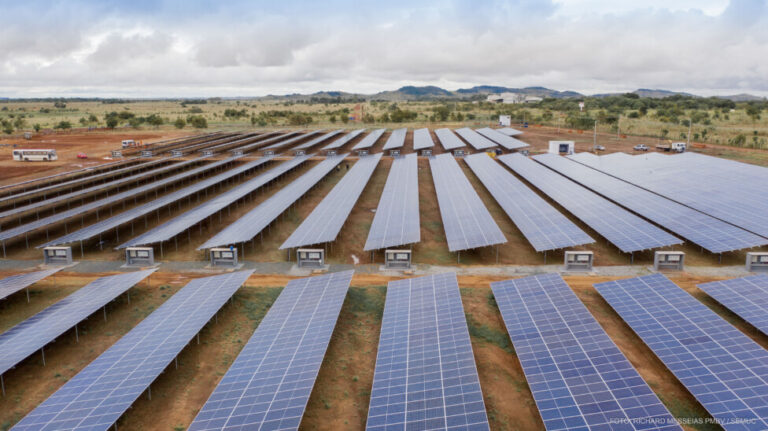
Solar panels have mushroomed on the roofs of public buildings and parking lots around the city. The largest unit was built on the outskirts of Boa Vista - a 15,000-panel power plant with an installed capacity of 5,000 kilowatts.
In the city, the parking lot of the Municipal Theater, a bus terminal, a market and the mayor's office itself stand out, covered with panels. There are also 74 bus stops with a few panels, but many were damaged when parts were stolen, Amorim told IPS in an interview in his office.
In total, the city had a solar power generation capacity of 6700 KW at the end of 2020, equivalent to the consumption of 9000 local households. It also promotes energy efficiency in the areas under municipal management.
"Eighty percent of the city is now lit up by LED bulbs, which are more efficient. The goal is to reach 100 percent in 2023," said the municipal secretary.

The mayor's office, during the administration of Teresa Surita (2013-2020), was a pioneer in the installation of solar power plants and also in comprehensive care for children from pregnancy to adolescence, for youngsters in the public educational system.
The city’s Welcoming Family program provides coordinated health, education, social assistance and communication services for mothers and children, from pregnancy through the first six years of the children's lives. The day-care centers are called Mother Houses.
In recent years, students in the local municipal elementary schools have performed above the national average, coming in fifth place in student testing among Brazil’s 27 state capitals.
This was an especially outstanding achievement because the influx of Venezuelan migrants more than doubled the number of students in Boa Vista schools in the last decade.
Despite this, the quality of teaching was not affected, according to the indicators of the Education Ministry’s Basic Education Evaluation System.

The results of the local early childhood policy have been recognized by several national and international specialized entities, including the United Nations Children's Fund, which awarded it the Unicef Seal of Approval in 2016 and 2020.
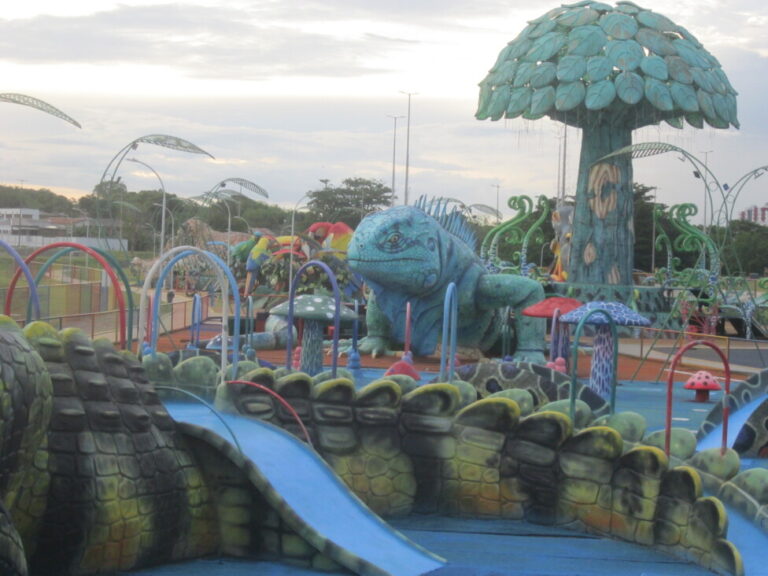
More visible than the solar panels are the 30 playgrounds of varying sizes scattered around the city, in some cases featuring large playground equipment and structures in the shape of national wild animals, such as crocodiles and jaguars. They are called "selvinhas" (little jungles).
The use of solar power has spread to other sectors of life in Roraima, a state with only 650,000 inhabitants, despite its large area of 223,644 square kilometers, twice the size of Honduras, for example.
In May, there were 705 solar plants in homes, businesses and private companies, in addition to public buildings, in the state, with a total installed capacity of 15,955 KW (just under one percent of the region's total).
In Roraima there are solar plants in the courthouses in four cities, in an aim to cut energy costs through a program called Lumen.
The Federal University of Roraima (UFRR) is also building a 908-panel plant, to be inaugurated by March 2023, with the capacity to generate 20 percent of the electricity consumed on its three campuses.
"The main objective is to save energy costs, and the goal is to expand to cover 100 percent of consumption. But it will also be useful for electrical engineering studies," Emanuel Tishcer, UFRR's head of infrastructure, told IPS.
The training of specialists in renewable sources, research into more efficient and cheaper panels, the comparison of technologies and innovations all become more accessible with the availability of an operating solar power plant, which serves the university's electrical energy laboratory.
Edinho Macuxi, general coordinator of the Indigenous Council of Roraima (CIR), the largest organization of native peoples in the state, said "the great objective (of solar energy) is to prove that Roraima and Brazil do not need new hydroelectric plants."
The Bem Querer (Portuguese for "good will") plant on the Branco River, Roraima's main river, "will have direct impacts on nine indigenous territories" and will also affect other nearby indigenous areas if it is built, as the central government intends, he told IPS.
That is why the CIR is involved in three projects - two solar energy and a wind energy study - in territories assigned to different indigenous ethnic groups, he said.
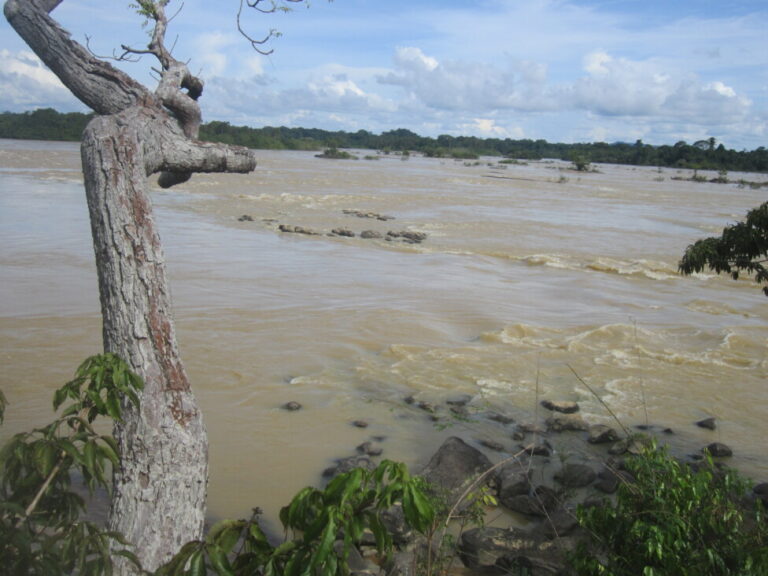

The government's hydroelectric plans, which currently prioritize Bem Querer, but include other uses of local rivers, have sparked a renewed debate on energy alternatives in Roraima, which has an installed electricity capacity of only 300 megawatts, since it has almost no industry.
From 2001 to 2019, Roraima relied on electricity from neighboring Venezuela, generated by the Guri hydroelectric plant in eastern Venezuela, the deterioration of which caused a growing shortage over the last decade, until the supply completely ran out in 2019, two years before the end of the contract.
Diesel thermoelectric plants had to be reactivated and new plants had to be built, including one using natural gas transported by truck from the Amazon jungle municipality of Silves, some 1,000 kilometers away, in order to guarantee a steady supply of electricity that the people of Roraima did not have until then.
It is costly electricity, but its subsidized price is one of the lowest in Brazil. The subsidy drives up the cost of electric power in the rest of the country. That is why there is nationwide pressure for the construction of a 715-kilometer transmission line between Manaus, capital of the state of Amazonas, also in the north, and Boa Vista.
With this transmission line, Roraima will cease to be the only Brazilian state outside the national grid, and local advocates believe it will be indispensable for a secure supply of electricity, a long-desired goal.

To discuss this and other alternatives, a group of stakeholders created the Roraima Alternative Energies Forum in September 2019, to promote dialogue between all sectors, in search of "the strategic construction of solutions to make the use of renewable energies viable in the state."
"Our focus is energy security. The Forum is focused on photovoltaic sources and distributed generation. But it seeks a variety of renewable energies, including biomass," said Conceição Escobar, one of the Forum's coordinators and president of the Brazilian Association of Electrical Engineers in Roraima.
"There is an opportunity for everyone to be involved in the discussion. The construction of transmission lines and hydroelectric plants takes a long time, we have perhaps ten years to develop alternatives," she told IPS.
"I am against Bem Querer, but the government of Roraima supports it. The Forum listens to all parties, it does not want to impose solutions. We want to study the feasibility of combined sources, with solar, biomass and wind, and encourage the use of garbage," said biologist Rosilene Maia, who also forms part of the three-member board of the Forum.
© Inter Press Service (2022) — All Rights Reserved. Original source: Inter Press Service
 Global Issues
Global Issues